Double-sided Laser Shock Peening
Abstract:
Laser Shock Peening (LSP) is a process that uses high-energy nanosecond laser pulses to generate compressive residual stresses in metallic materials. These materials then exhibit longer fatigue life and generally higher resistance to cracks of all kinds. The standard method of applying LSP is to focus the laser beam on one side of the sample in the area where cracks usually initiate.
When compressive residual stresses are generated, the residual stresses in the sample are redistributed. This results in compression in the target area, while tension is created around and below this area. If the sample is thin (< 7 mm), the redistribution of stress can cause macroscopic bending of the sample away from the affected area.
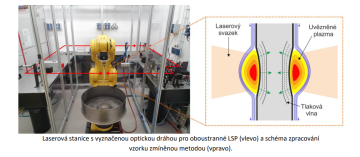
This geometric deformation of the sample is generally undesirable from an application perspective, and the deflection on one side must be compensated for by the same deflection on the other side by treating the opposite side of the sample. However, this method is not very accurate and cannot be used for components such as turbine blades, which require high precision. Therefore, the so-called double-sided LSP method is chosen, in which the same laser beams strike the sample or component from both sides simultaneously. Pressure is then applied to both sides of the material at the same time, and no geometric deformation occurs.
The aim of this work is to put the double-sided LSP method into practice at the HiLASE center. The LSP station currently has a U-shaped optical table that enables this method, but so far only one side of the table has been used.
The student would split the laser beam into two and set up an optical path on the other side of the table. The optical path will need to be dimensioned so that the beam reaches the sample from both sides simultaneously.
Given the nature of the topic, a certain degree of manual dexterity and interest in practical work with laser beams and optical and optomechanical elements is expected. One of the outputs of the work will also be a comparison of the original one-sided LSP with the new two-sided approach. The determining factor will be the geometric accuracy of the processed samples.
What do we offer?
- Flexible working hours adapted to your class schedule
- Hands-on experience with advanced laser technologies
- Expert guidance and mentoring from experienced researchers
- Access to a modern laboratory and a friendly team of colleagues
Number of vacancies for this topic: 1
Supervisor: Doc. Ing. Ladislav Pína, DrSc.
Consultant: Ing. Jan Kaufman, Ph.D.
Field: Physics, Applied Research
Type of work: Diploma thesis
Training workplace: HiLASE, Institute of Physics, Czech Academy of Sciences
Language: Czech, English
Location: Dolní Břežany
Join us and step into the fascinating world of lasers!
If you think we could work well together, send me your CV and a few words about why you would like to do an internship with us.
I look forward to hearing from you!
Jan
Please always include the following text with your email/letter so that we can process the information you send us:
I agree that my personal data sent to FZU AV ČR, v.v.i., with its registered office at Na Slovance 2, 182 21 Prague 8, may be used in accordance with Act No. 110/2019 Coll. exclusively for the purposes of job placement and maintaining a database of job applicants. This consent is given for a period of one year and can be revoked in writing at any time.
Contact
